WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING? A DEEP STUDY OF CLOUD COMPUTING
The idea
of the cloud is no longer a total riddle. It’s a term used so much in every aspect of
digital metamorphosis and new-age technology that we’ve accepted that the cloud is going
to be a part of everyday life—indeed, if the accusations of the cloud shift aren’t yet
totally grasped. But not understanding the structure of cloud computing and what it
affords us means we’re taking this essential technology for granted.
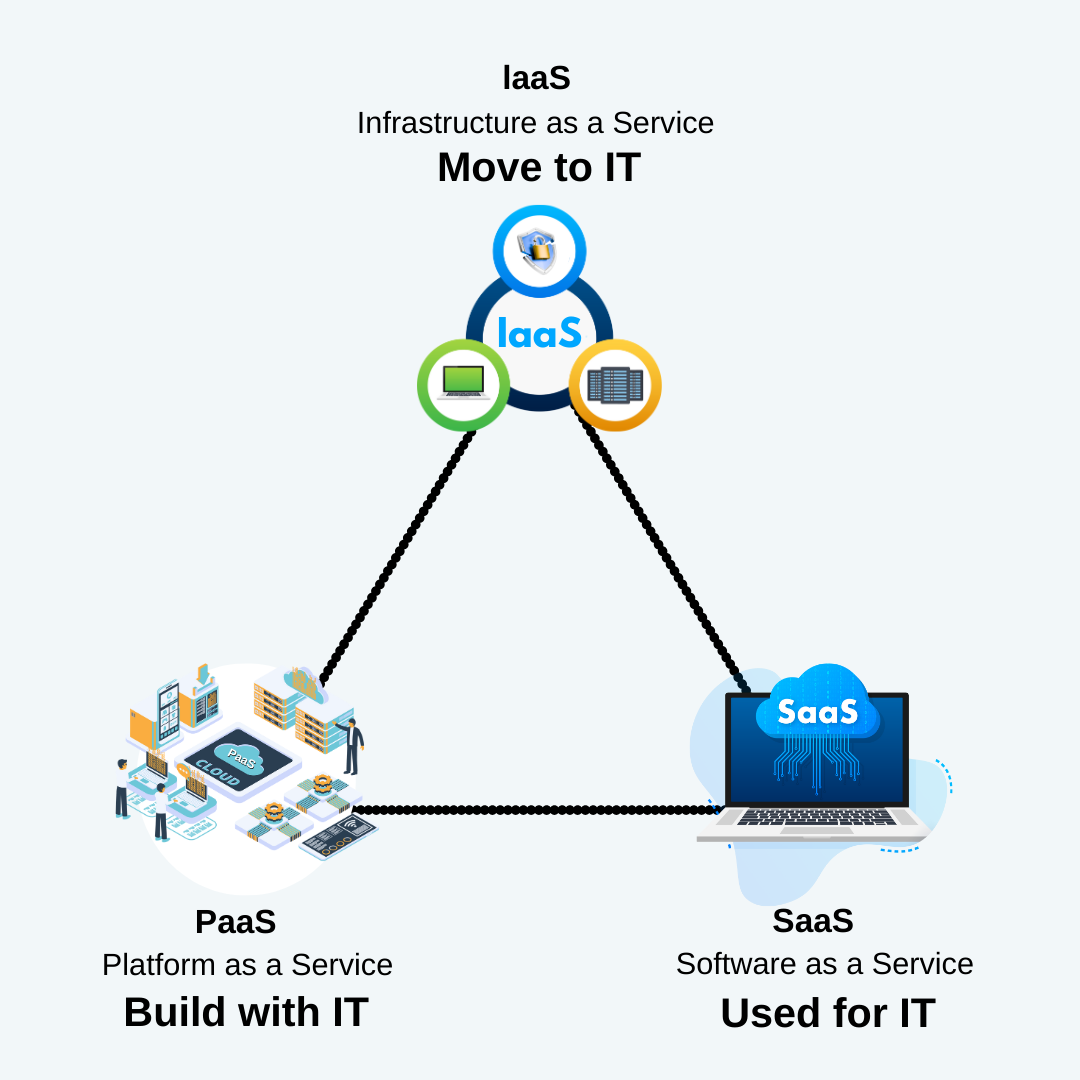
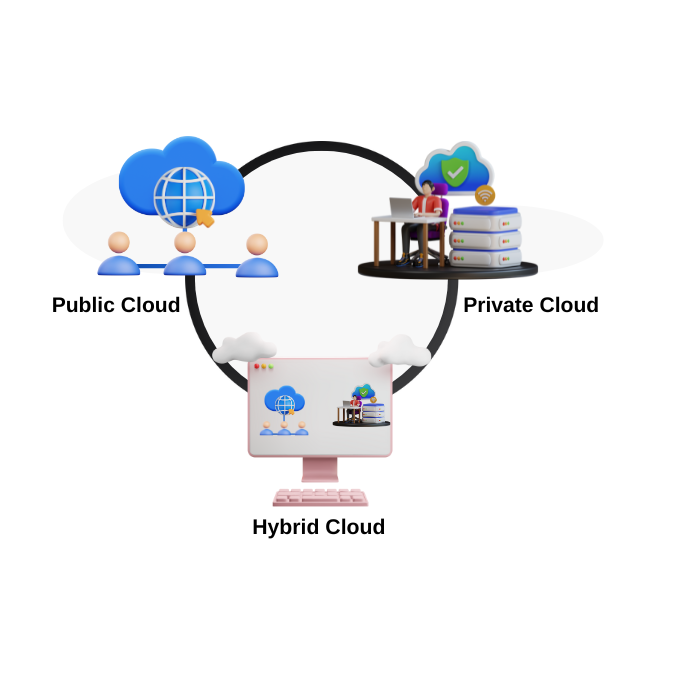
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is
the on-demand delivery of IT funds over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Rather than buying,
retaining, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services,
similar to calculating power, storage, and databases, on an as-demanded basis.
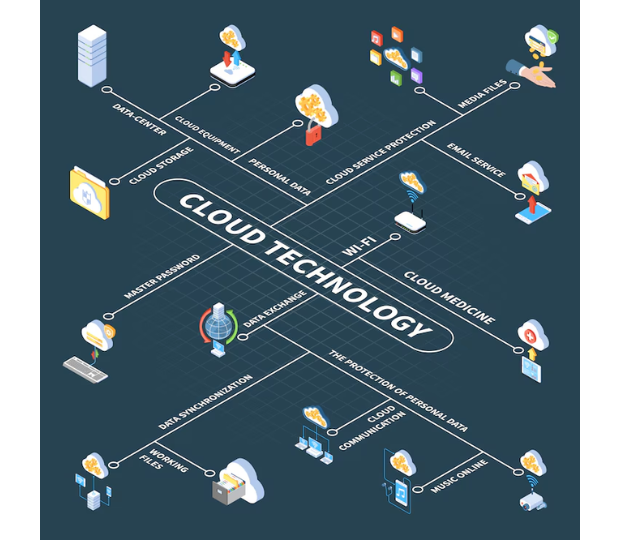
And while there are several different ways to define cloud computing, it all comes down to these
five key aspects:
- Networking 1.
- Data Management 2.
- Storage 3.
- Services 4.
- Devices 5.